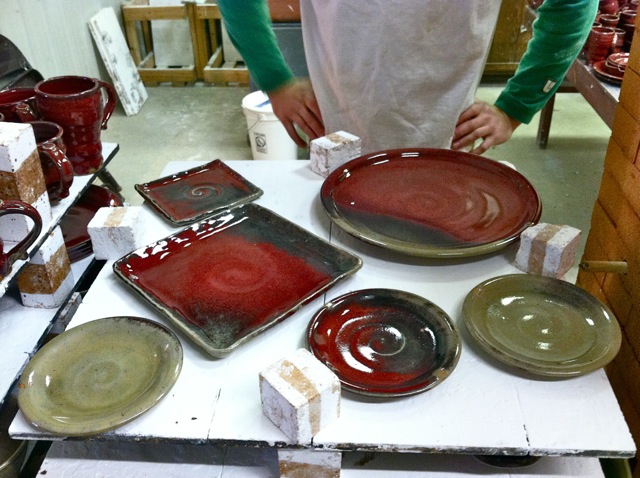
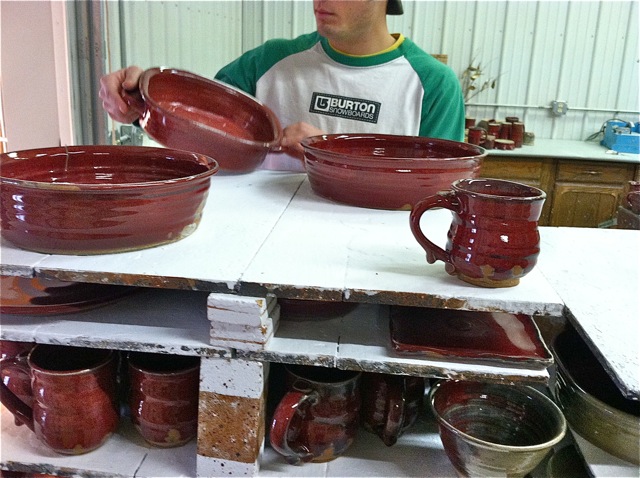
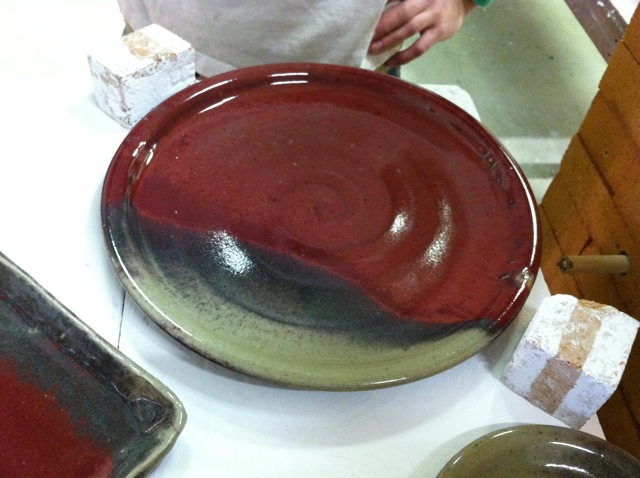
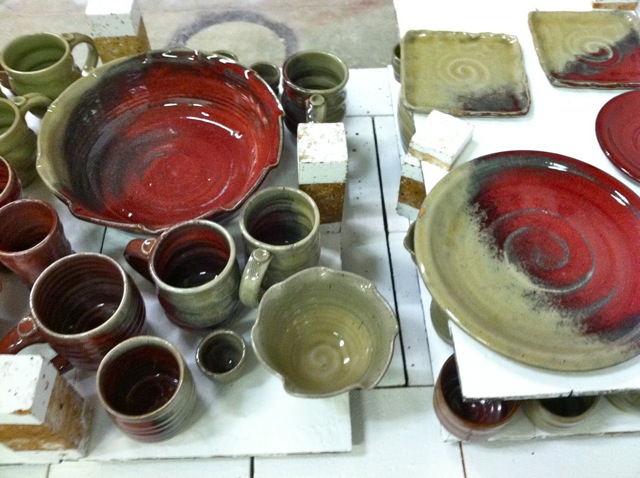
The Nuka glaze originated in Japan centuries ago. Potters traditionally made the glaze by using ashes from burnt rice hulls. These ashes were high in Silica, which is a glass former, so some Nuka glazes could be made with almost entirely ash.
Phil Rogers describes the Nuka glaze in his book “Ash Glazes” along with a huge variety of other glazes. I learned many of my glazing techniques from this book, like creating custom glazes from raw materials which is how I develop all of my glazes.
Check out the awesome Nuka glazed bottle below, made by Japanese folk potter Shoji Hamada. He was renowned for making skillfully crafted pottery inspired by his natural surroundings, and made with natural materials that he harvested locally. This Nuka was made with 50/50 ash and stone, and a black Tenmoku was brushed over.

Ash as a Glaze Ingredient
Every other year, I pick up about 200 gallons of wood ash from my friend who heats his family’s home with wood furnace. He harvests most wood from deadfall trees in the St. John’s Arboretum. I like using this ash because it’s a natural material that I can get from a local waste source. It’s also free, but takes a lot processing to get rid of all the charcoal and debris. The image below shows some tools I made to sift the ashes through 12, and then 40 mesh screens.

Developing Glaze Recipes
I’ve spent about three years developing recipes for my Nuka glaze. Technically, it many not be a ‘Nuka’ anymore due to all the materials I’ve added. I still call it a Nuka because I’m inspired by the materials and surfaces used historically, but my glaze has become pretty complex.
Traditionally, Nuka glazes were fired hotter than most glazes. While I was still in school at CSB/SJU, my professor Sam Johnson and I got great results with the Nuka when firing upwards of cone 12, or over 2500 degrees F. Since graduation, I’ve lowered the temperature to cone 10, or just under 2400 degrees F. I did this by using line blend testing. I could write another blog post on line blend glaze testing, so for now I’ll just refer you back to Phil Rogers, “Ash Glazes.”
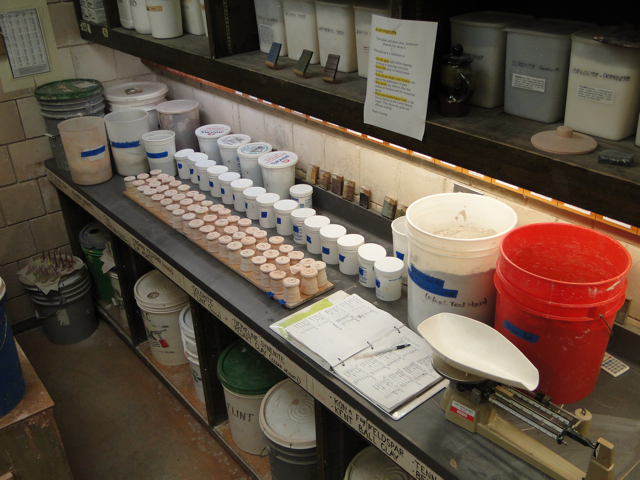

For all you potter readers, here’s my Glossy Nuka glaze recipe for cone 10. If you dry-sift ashes through a window screen you could probably get similar results. I keep this glaze at about 145 specific gravity to keep it from dripping off the pots:
| Glossy Nuka | Parts | Percentage |
| Wood Ash – dry sifted | 33 | 18.5 |
| Custer Feldspar | 50 | 28.1 |
| Silica (325 mesh Flint) | 30 | 16.9 |
| Frit 3134 | 15 | 8.4 |
| Whiting (High Purity) | 20 | 11.2 |
| Bone Ash | 10 | 5.6 |
| Bentonite | 10 | 5.6 |
| Talc | 10 | 5.6 |
| total | 178 | 100.0 |
Brushing Iron and Cobalt
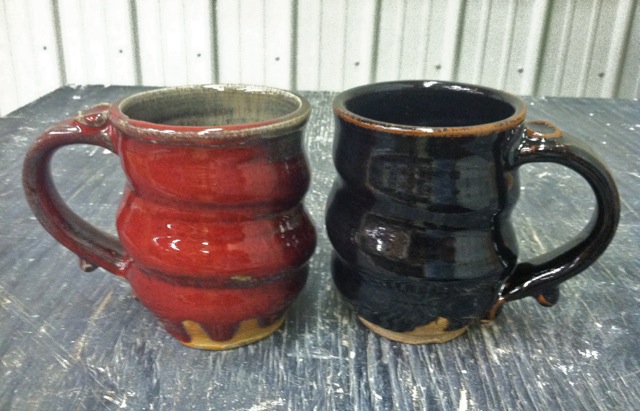
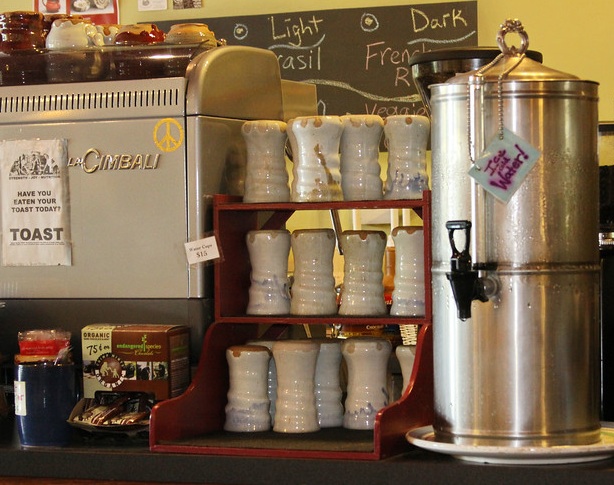
I accent each pot with iron or cobalt washes on the rim. These naturally drip down each pot during the firing, creating a surface that reminds me of wet paint. I like to think of each pot as a canvas for glaze. The cup on the left was also electric fired at cone 10, while the mug on the right was gas fired. I think that the extreme oxidation of the electric kiln contributes to the crystal growth in the cup, which is highlighted by the iron as yellow specks.
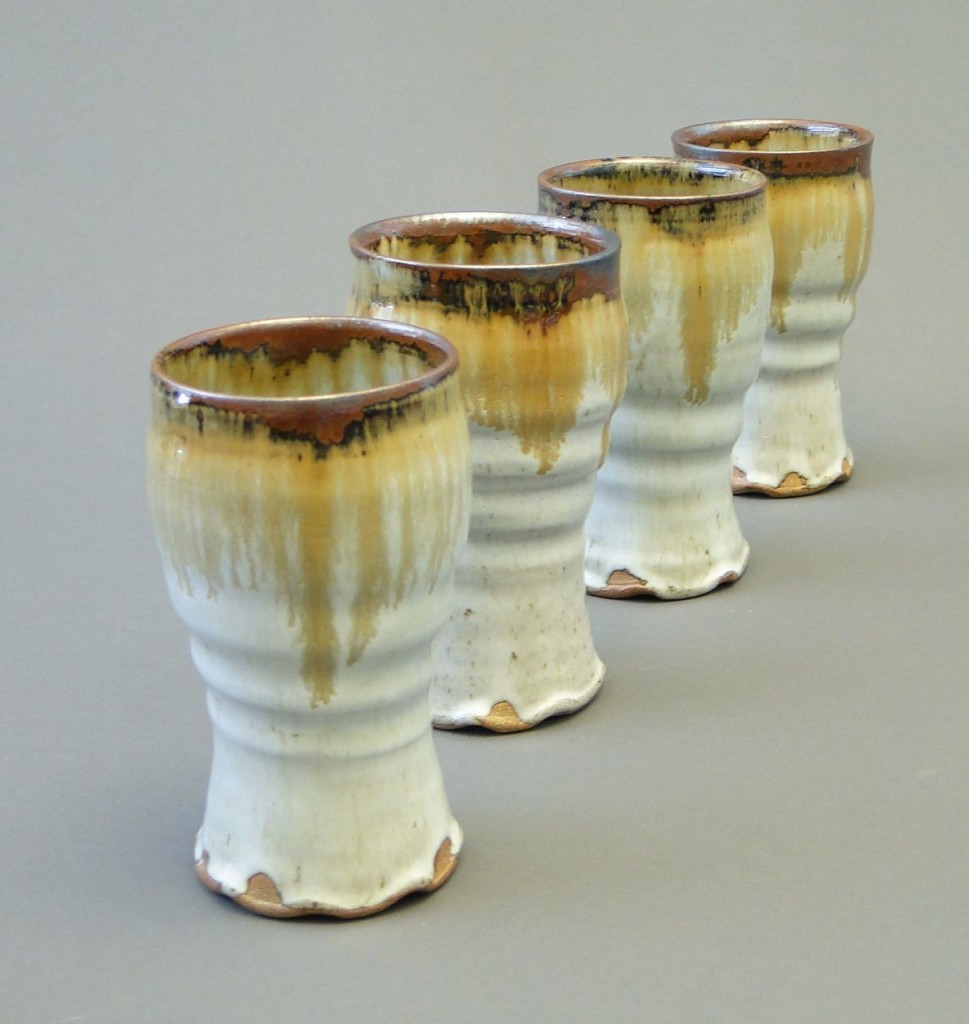
The cups above were gas fired at cone 13, back in 2011. This is one of my favorite versions of the Nuka because of the glossy, milky surface and the color complexity of the iron drips. I’ve spent years adapting my new recipes to reproduce this surface, and I’ve discovered a huge variety of colors and textures within the Nuka color pallet. The lower cone 10 temperature has been a good challenge for this glaze, and I hope to develop a cone 6 Nuka in the near future.
I’m also exploring more ways the Nuka relates to my other 2 glaze choices: Copper Red and Tenmoku:
*Added November, 2016:
To view the most recent evolution of my Nuka Glazed “Standard Ware” pots, including “Nuka Cobalt” and “Nuka Iron” color pallets, view our online store: store.cherricopottery.com/standard-ware